Wireless Internet
Long range connectivity
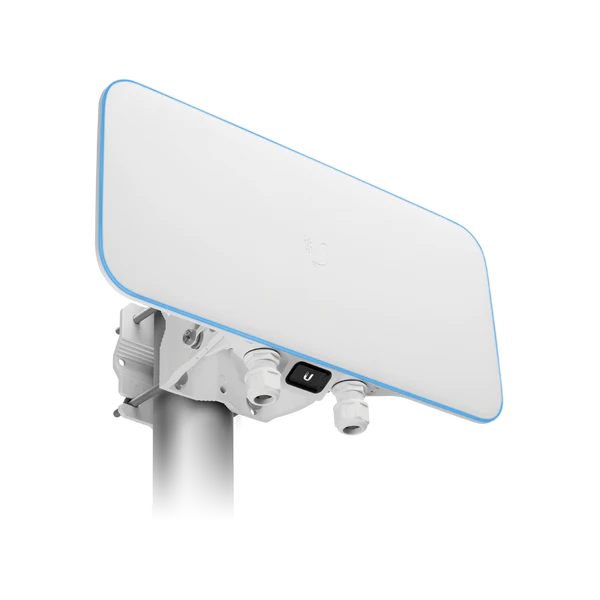



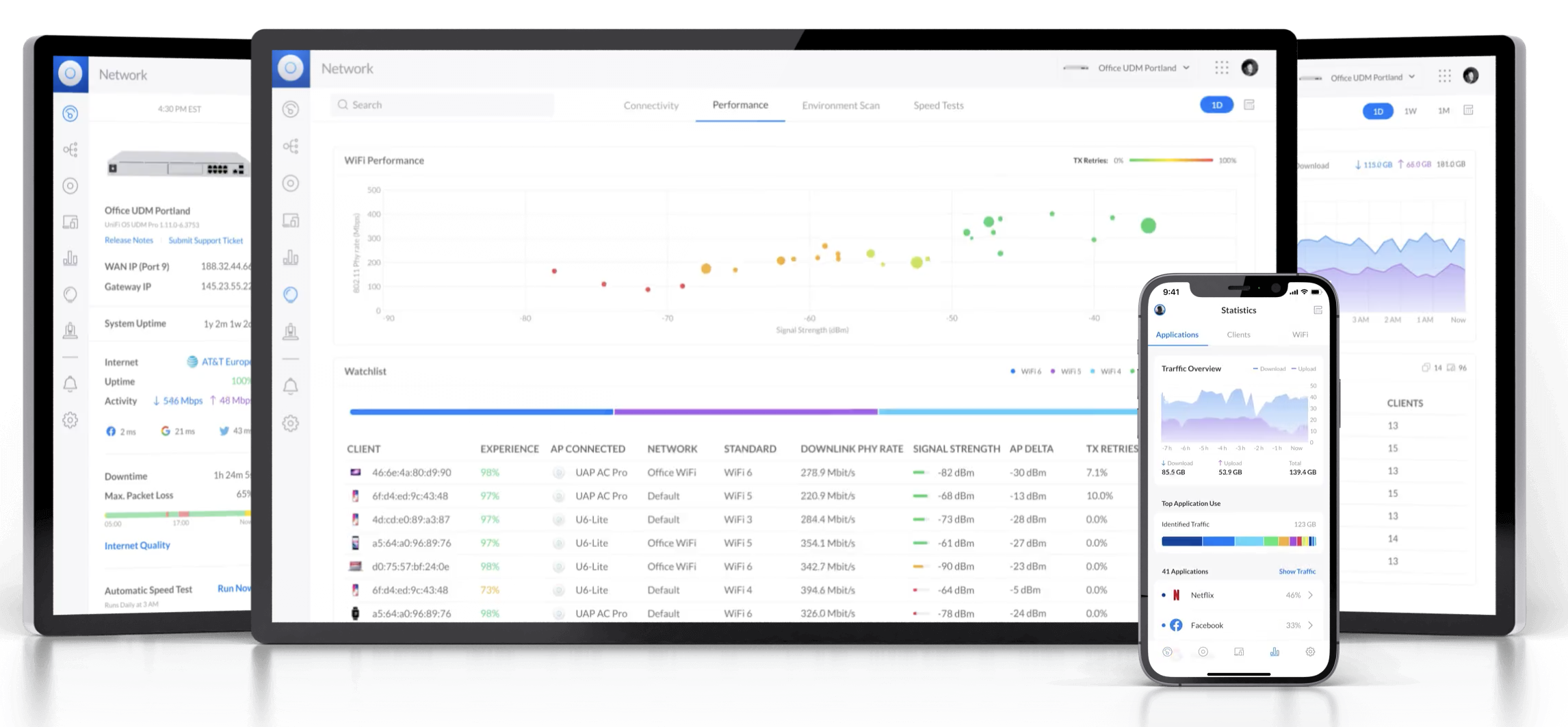
Long-range WiFi networks are designed to extend the reach of wireless internet connectivity over greater distances than standard WiFi systems. Here are some key points about long-range WiFi networks:
- . **Technology**: Long-range WiFi often utilizes advanced technologies such as WiFi 5 (802.11ac) or WiFi 6 (802.11ax), which provide better coverage and faster speeds. These technologies can efficiently handle multiple devices and reduce interference.
- 2. **Higher Power Transmitters**: Long-range networks often use WiFi access points with higher transmission power and specialized antennas that can project signals over longer distances effectively.
- 3. **Directional Antennas**: Using directional antennas, such as Yagi or parabolic antennas, can significantly increase the range of a WiFi signal by focusing the signal in a specific direction rather than broadcasting it in all directions.
- 4. **Mesh Networks**: Implementing a mesh network can extend coverage by using multiple access points that communicate with each other, providing seamless WiFi over larger areas without dead zones.
- 5. **Repeaters and Extenders**: WiFi repeaters and extenders can boost the signal strength and extend the range of an existing wireless network. They can be placed at strategic locations to cover areas with weak signals.
- 6. **Frequency Bands**: Long-range networks may operate on the 2.4 GHz band, which has a longer range but slower speeds, or the 5 GHz band, which offers faster speeds but shorter range. Balancing both bands can enhance overall network performance.
- 7. **Outdoor Installation**: Long-range networks are often used for outdoor applications, such as connecting rural areas, extending coverage in parks, and providing WiFi in large campuses or industrial sites.
- 8. **Site Survey**: Conducting a site survey helps determine the best locations for access points and antennas. It assesses factors like obstacles, interference, and required coverage areas.
- 9. **Challenges**: Obstacles such as buildings, trees, and other structures can affect signal strength and quality. It’s important to plan the placement of equipment carefully to minimize interference.
- 10. **Applications**: Long-range WiFi networks are common in various settings, including rural broadband, enterprise environments, outdoor venues, and smart city initiatives.
By leveraging these technologies and strategies, businesses and organizations can effectively implement long-range WiFi networks to ensure robust connectivity over expansive areas.